You would need 6 chargers to form a ring as per the diagram below:
Solution of the Week #457 - Sloping Square
The first thing we need to is to establish the length and width of the rectangle, let’s call them x and y respectively. We can make use of the fact that the small triangle above the 196 square is similar to the large triangle to the right of it. Since 14^2=196, the side length of the square is 14, and so:
(x-14)/14 = 14/(y-14)
(x-14)(y-14) = 196
xy-14(x+y)+196 = 196
But we already know that xy=882, as that is given in the question,
882 = 14(x+y)
x+y = 63
Knowing the sum and product of x and y we could solve as a quadratic, but I’m going to use the similar method of middle and difference. m is the middle of x and y, and is therefore 31.5, and d is the amount by which x is greater than m and y is less than m.
(m+d)(m-d)=882
m^2-d^2=882
d^2=m^2-882
d=10.5
And so therefore x and y are 42 and 21 respectively.
Now looking at the other half of the rectangle, the triangles surrounding the sloping square are also similar to the two in the lower half, and will have legs in the ration of 42 to 21, or 2 to 1.
Looking along the diagonal, if we call the side length of the sloping square ‘s’, we find that 2s + s + s/2 makes up the diagonal, which has an overall length of sqrt(42^2+21^2) = 21*sqrt(5).
So 3s/2 = 21*sqrt(5)
s = 6*sqrt(5)
The area of the sloping square is s^2, which is 180.
Solution of the Week #456 - Trigonometry Conundrum
Draw a line between the top of the left triangle and the top of the right triangle.
The length (d) of this line is √(a2+b2), and the angle (α) at the top of the left triangle is arctan(b/a).
The angle between this new line and the vertical is (α+θ).
Sliding this line down by the height of the right triangle forms a triangle with the left and lower lines, without changing the angle or the length d.
Therefore arcsin(c/d) = (α+θ), or θ = arcsin(c/d)- α
Or written out in full:
θ = arcsin(c/√(a2+b2))- arctan(b/a)
Solution of the Week #455 - Triangle
Let’s call the a+3 length ‘c’ and the base ‘B’.
The area of the triangle is half base times height, and that can be done in two different ways, so ac = 4B.
Using Pythagoras, c^2 + a^2 = B^2
Let’s expand (c-a)^2:
(c-a)^2 = c^2 + a^2 – 2ac
But we know that (c-a) is equal to 3, and we know the values of c^2+a^2 and ac in terms of B, so:
9 = B^2 – 8B
Solving this quadratic we get B is 9 or -1. As it’s a length it must be positive, so the base B is equal to 9.
If you’re interested, the value of a is 3(sqrt(17)-1)/2, which is about 4.68.
Solution of the Week #454 - Heptagon Circle Maximisation
So to solve the heptagon puzzle, we would hope to reduce it to this case: a bite made of two equal lines, which we can then solve by letting the vertex lie on the circle centre. We want to deform the four edges of the heptagon to two equal lengths, whilst maintaining the two endpoints where it meets the circle, and also maintaining the area of the heptagon.
If I draw an line between two non-adjacent vertices, then draw a parallel line through the vertex between them, and extend the next edge of the heptagon to meet that parallel line, and then move the middle vertex to that new intersection, then the area is preserved, but the number of edges has been reduced. I can do the same thing again to reduce the cut to two edges:
Finally to make those two edges equal, I draw a line between the two fixed vertices, drop a perpendicular bisector, and find the intersection between that and the parallel line through the remining internal vertex.
Finally, centring the circle on this point relative to the heptagon and rescaling the figure so that the arc length is equal to 1, we do indeed find this to give the maximum area, which is approximately equal to 0.0942943...
Solution of the Week #453 - The Long Game
You will find that you have to take the second day off, since you can’t play the same letter as day one, but you also can’t play another card for the first time. At the very end of the game, when you only have one card to play, you must again take a day off, since it will either be following the 6th playing of the same letter, or the 7th playing of a different letter. However these are the only days off you will need to take, and so you can play all 98 cards in 100 days.
For example (underscore denotes a day off, spaces are inserted for readability):
A_AB ABC ABCD ABCDE ABCDEF ABCDEFG BCDEFGH CDEFGHI DEFGHIJ EFGHIJK FGHIJKL GHIJKLM HIJKLMN IJKLMN JKLMN KLMN LMN MN_N
Solution of the Week #452 - Find the Radius
Firstly notice that the two smaller triangles are identical, and that the height of each of them is the same as the height of the rectangle. If we call the radius of the blue circle ‘r’, then a small triangle is 4r tall. Let’s work out what the base is:
Using Pythagoras: (ar+3r)^2 = (ar+r)^2 + (4r)^2
Divide throughout by r^2 and multiply the brackets:
a^2+6a+9 = a^2+2a+1+16
4a = 8, a=2, therefore the base of the small triangle, and so also of the rectangle, is 3r.
Now let’s look at a small section within the rectangle:
Using Pythagoras again on the right-angle triangle in the middle of this figure:
r^2+18r+81 = r^2 + (9/4)r^2-27r+81
18r = (9/4)r^2-27r, since we know r is not equal to 0 we can divide throughout by r:
45 = 9r/4, r = 20.
So the radius of the blue circles is 20.
Solution of the Week #451 - Answer Sequence
ELF – FILE – LIFER – RIFFLE – FIREFLY (or the reverse order)
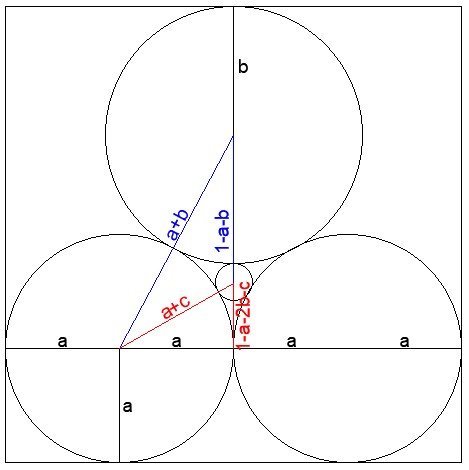
Solution of the Week #450 - Small Circle
Let’s call the radius of the pair of identical circles ‘a’, the radius of the top circle ‘b’ and the radius of the small circle ‘c’ (the value we ultimately seek).
Since 4a = 1, a = 1/4.
Using Pythagoras on the blue triangle
(a+b)^2 = (1-a-b)^2 + a^2
a^2 + 2ab + b^2 = 1 – 2a – 2b + 2ab + a^2 + b^2 + a^2
2b = 1 – 2a + a^2
Substituting our known value of a = 1/4:
2b = 1 – 1/2 + 1/16
b = 9/32
Using Pythagoras on the red triangle:
(a+c)^2 = (1-a-2b-c)^2 + a^2
Let’s substitute our known values for a and b straight away:
(1/4+c)^2 = (3/16-c)^2 + 1/16
1/16 + c/2 + c^2 = 9/256 – 3c/8 + c^2 + 1/16
c(1/2+3/8) = 9/256
c = 9/256 * 8/7
c = 9/224
Solution of the Week #449 - Swap Grid
The reason the number grid takes 20 swaps is that it can be split into five cycles of 5 (for instance, 1,8,15,17,24 is a cycle). A cycle of n cells can be solved in n-1 swaps, so each of the cycles takes 4 swaps to solve.
In the letter grid, you want to find smaller cycles if possible. It turns out you can find four cycles of 2 letters each (where a single swap would solve both letters), three cycles of 3 letters, and two cycles of 4 letters, as coloured below. This will take 16 swaps in total.
To advance the solution, swaps should only be made within those minimum cycles (in the number grid, since 1 and 15 were in the same cycle, swapping them advanced the solution, without solving either letter in the swap, although it did change a 5-cycle into a 2-cycle and a 3-cycle).
In the letter grid, if any swaps were made within the 2-cycles or 3-cycles, letter would be solved, so we need to look only at the 4-cycles. Swapping one pair within each of the two 4-cycles as shown will turn each 4-cycle into two 2-cycles, advancing the solution without solving any letters, so the answer to the bonus question is 2.
Solution of the Week #448 - 2023 2024 Puzzle
Calling the sum of the two square roots ‘S’, and the difference of the two square roots ‘D’, the expression becomes S*sqrt(D/S)
We notice that S*D is a difference of two squares and is therefore equal to 2024-2023, which is 1.
If we take the fraction under the square root, we can multiply top and bottom by D without changing its value. The top becomes D^2 and the bottom becomes 1. Then the square root of a square means that the whole square root expression can be replaced with D. Then the entire expression is just S*D, which of course is just 1.
The numbers 2024 and 2023 in this puzzle are unimportant; what’s important is that the first is one more than the second.
Solution of the Week #447 - New Order
Lioness
Network
Freighter
Zaniness
Antenna
If you remove the first two letters and the last two letters of each word you get a number. The words are now placed in numerical order based on those numbers.
Solution of the Week #446 - Pentagon to Square
Perform straight cuts from each of the right-angle vertices to the midpoint of the base. Hinge the two wing parts around to be above the original top vertex of the pentagon, as below:
Solution of the Week #445 - Functional Equation
As we’re hoping to evaluate f(4) we might try letting x = 4 initially:
2*f(-3) – f(4) = 540
But now we need to know the value of f(-3), so:
2*f(1/2) - f(-3)= -405
We plough on:
2*f(6/5) - f(1/2) = 135/2
2*f(5/3) - f(6/5) = 162
2*f(9/4) - f(5/3) = 225
And just as we start to lose hope:
2*f(4) - f(9/4) = 1215/4
So now we have 6 equations in 6 unknowns, let’s multiply the second equation by 2, the next by 4, the next by 8 etc:
2*f(-3) - f(4) = 540
4*f(1/2) - 2*f(-3) = -810
8*f(6/5) - 4*f(1/2) = 270
16*f(5/3) - 8*f(6/5) = 1296
32*f(9/4) - 16*f(5/3) = 3600
64*f(4) - 32*f(9/4) = 9720
Adding all of these together cancels out all of the f() terms except for f(4):
63*f(4) = 14616
Therefore:
f(4) = 232
Solution of the Week #444 - Pascal's Ladder
The bottom row will be 22081485, the 22nd of August 1485, the date of the Battle of Bosworth Field.
Solution of the Week #443 - Find the Value
(2x+3)(3x+4)(4x+5)=11
You could of course multiply the backets together and solve the resulting cubic, but I’m going to use a different method:
I note that the coefficients of x are 2, 3 and 4, and the least common multiple of those is 12, so I will multiply each bracket in order that those coefficients match (and multiply the right side by the same amount to retain equality):
(12x+18)(12x+16)(12x+15)=11*6*4*3
Next I’m going to change the variable by letting u=12x+18
u(u-2)(u-3)=11*9*8
Note I also re-factorised the right-hand side to match the format, which allows me to say that u=11. Since we are only looking for one real solution, we are now on the way to finding it:
12x+18=11
12x=-7
x=-7/12
Putting that value back through the equation confirms that this is the correct value.
Solution of the Week #442 - Triangle on a Square
A trial and error method is a good way to approach this particular puzzle, plugging in different potential values for DE, calculating DF from the similar triangles DEF and CEB, then calculating the area and perimeter of DEF. You will soon find that DE=8, DF=6, and the area and perimeter of DEF is 24.
For a more systematic approach, I used the nice fact, easily proved, that a triangle has the same area and perimeter if and only if the radius of its incircle is equal to 2. So putting in place a coordinate system where B is the origin, I place a circle of radius 2 at (22,26). Then, because I need EFB will be tangent to this circle, I construct another circle, centred on (11,13) and passing through the origin. Using the formulae of the two triangles to work out where they coincide*, I can find the point on line EFB has position (20.4,27.2). This enables me to find the position of point E to be (24,32), and the area and perimeter of triangle DEF to be 24.
Solution of the Week #441 - Puzzle 441
Each number from 1 to 441 must pair with two other valid numbers to add to two of target sums 321, 442 or 763, as the sequence goes to a number and then away from it again. For example, 13 would pair with 308, 429 and 750 to form the target sums. 750 is outside of the range of numbers in the sequence, so therefore 308 and 429 must be either side of 13 in the sequence. This is true for every number except for the numbers at the very ends of the sequence, which can only for a valid pair adding to ONE of the target sums. These are 321, which would pair with 0, 121 and 442 to form the target sums, and only 121 is in the range 1-441. At the other end of the sequence will be 221, which pairs with 100, 221 or 542. 542 is outside of the range, and 221 is the same number again, so 100 must be adjacent to 221. So 221 and 321 are at the ends of the sequence.
It's not obvious, and I won’t go into the reasons here, but at the exact middle of the sequence will be the average of those two end numbers, 271.
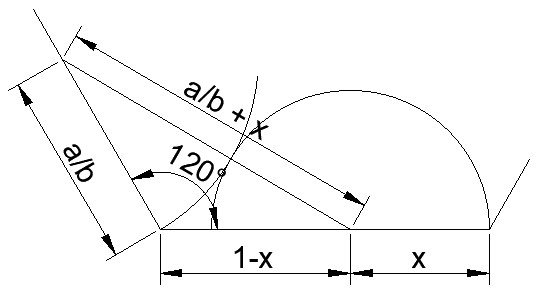
Solution of the Week #440 - Semicircles in a Hexagon
Let’s look at a general case where the previous radius is a/b and we wish to find the next radius x.
Using the cosine rule on the triangle shown, and taking advantage of the fact that cosine of 120 degrees is -0.5, we get:
(a/b + x)^2 = (a/b)^2 + (1-x)^2 + a/b(1-x)
(a/b)^2 + 2ax/b + x^2 = (a/b)^2 + 1 - 2x + x^2 + a/b – ax/b
2ax/b = 1 - 2x + a/b – ax/b
(2 + 3a/b)x = 1 + a/b
x = (1 + a/b)/(2 + 3a/b) = (a+b)/(3a+2b)
so assuming a and b are integers, x will be a rational number.
We can repeatedly use this formula starting from Ra = 1/2.
Rb = 3/7, Rc is 10/23, Rd = 33/76 and finally Re = 109/251. If you are curious, these fractions are converging on a value of
(sqrt(13)-1)/6.
Solution of the Week #439 - Odd Primes
p=13, q=r=3, s=5
p=13
p+5=18 is divisible by q
therefore q=3
q+6=9 is divisible by r
therefore r=3
r+7=10 is divisible by s
therefore s=5
s+8=13 is divisible by p